This section explains how Qumulo Alerts monitors alarms and alerts for a Qumulo Cluster.
How Qumulo Alerts Works
Qumulo Alerts is a Docker-based system that comprises multiple containers. The main container uses a series of plugins to collect hardware alarms and software alerts from Qumulo clusters.
In Qumulo Alerts, producers are Docker containers that take data from various sources, pass it through the Exchange, a processing queue, and finally give the data to consumers, defined users or user groups. In addition to processing data, the Exchange facilitates the transfers between the producers and consumers.
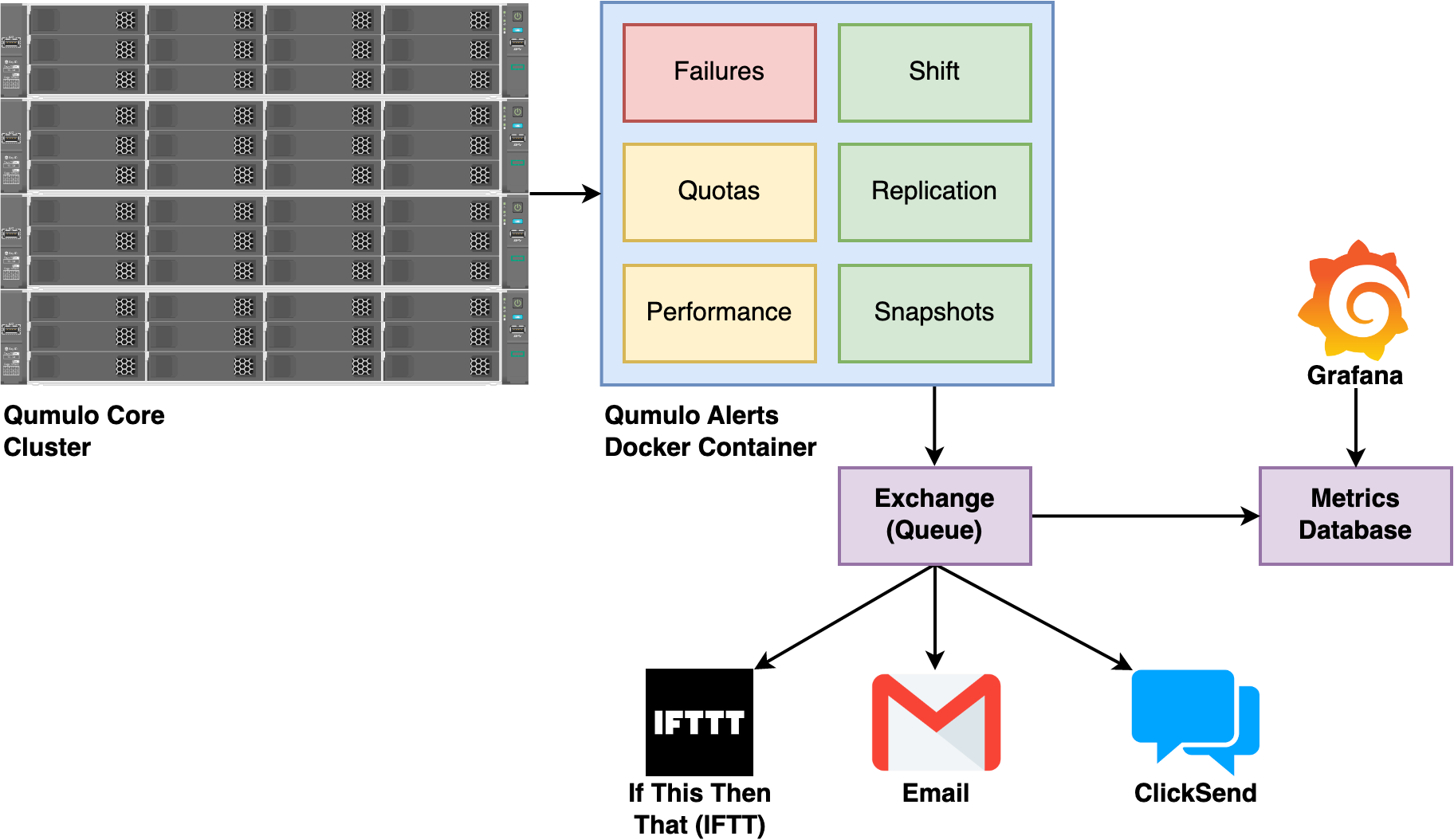
Both producers and consumers use plugins that help process alarms and alerts from a Qumulo cluster. A plugin is a mechanism that processes a single function, such as fan failure, disk failure, or node failure. Plugins help with granular control over the information that Qumulo Alerts collects and processes.
Working with the alerts CLI
The alerts CLI lets you configure Qumulo Alerts. For more information, use the --help flag.
Qumulo Alerts includes a CLI for the following operating systems:
- Ubuntu 20 and 22
- Red Hat Enterprise (RHEL) 8
- macOS
- Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10 and 11
Known Limits
This section lists the currently known limitations for Qumulo Alerts.
-
Floating IP Addresses or Network Load Balancing (NLB): To prevent overloading any node in a Qumulo cluster, Qumulo Alerts plugins connect to all nodes in the cluster by using floating IP addresses or an NLB.
Important
Qumulo Alerts can’t function if neither IP addresses nor NLBs are configured. -
Error Logging: Qumulo Alerts generates a large number of error messages that can help you debug issues. However, currently, all logging remains within the Docker container and is therefore not accessible easily. For help with troubleshooting issues, contact the Qumulo Care Team.
