This section explains how to wire NIC ports on HPE Alletra 4110 nodes and how to network a cluster.
Tip
To identify the
To identify the
eth port, run the following command:for i in /sys/class/net/eth*; \
do echo $i; \
cat $i/device/uevent | \
grep -i pci_slot; \
doneNode NICs and Ports
Important
Your HPE Alletra 4110 node uses a split networking configuration. Ensure that the front-end and back-end networks are connected and operational before creating your cluster. If only one of the networks is connected and operational during the cluster creation process, Qumulo Core deploys with the unified networking configuration.
Your HPE Alletra 4110 node uses a split networking configuration. Ensure that the front-end and back-end networks are connected and operational before creating your cluster. If only one of the networks is connected and operational during the cluster creation process, Qumulo Core deploys with the unified networking configuration.
The following diagrams show the NICs and ports on HPE Alletra 4110 node types.
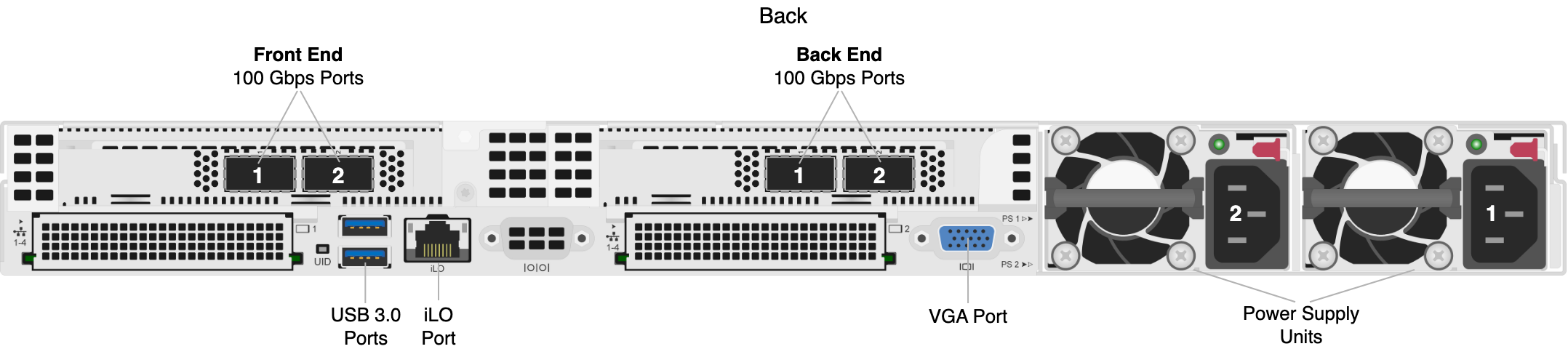
Prerequisites
- A network switch with the following criteria:
- 100 Gbps Ethernet connection
- Fully non-blocking architecture
- IPv6 compatibility
- Compatible network cables
- A sufficient number of ports for connecting all nodes to the same switch fabric
- One static IP for each node, for each defined VLAN
Important
Before you connect any Qumulo-supported equipment to your network, we strongly recommend consulting with your network engineering team.
Before you connect any Qumulo-supported equipment to your network, we strongly recommend consulting with your network engineering team.
Recommended Configuration
- One set of redundant switches for the front-end network, with an MTU that matches that of the clients that use the storage cluster. Typically, we recommend 1,500 MTU but in some instances 9,000 MTU is the optimal setting.
- One set of redundant switches for the back-end network (9,000 MTU minimum)
- One physical connection to each redundant switch, for each node
- One Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) port-channel for each network (front-end and back-end) on each node with the following configuration:
- Active mode
- Slow transmit rate
- Trunk port with a native VLAN
- DNS servers
- Network Time Protocol (NTP) server
- Firewall protocol or ports configured for Qumulo Care Proactive Monitoring
- Where
Nis the number of nodes, up to 10N-1floating IP addresses for each node, for each client-facing VLAN - Nodes connected at their maximum Ethernet speed (this ensures advertised performance). To avoid network bottlenecks, Qumulo validates system performance with this configuration by using clients connected at the same link speed and to the same switch as the nodes.
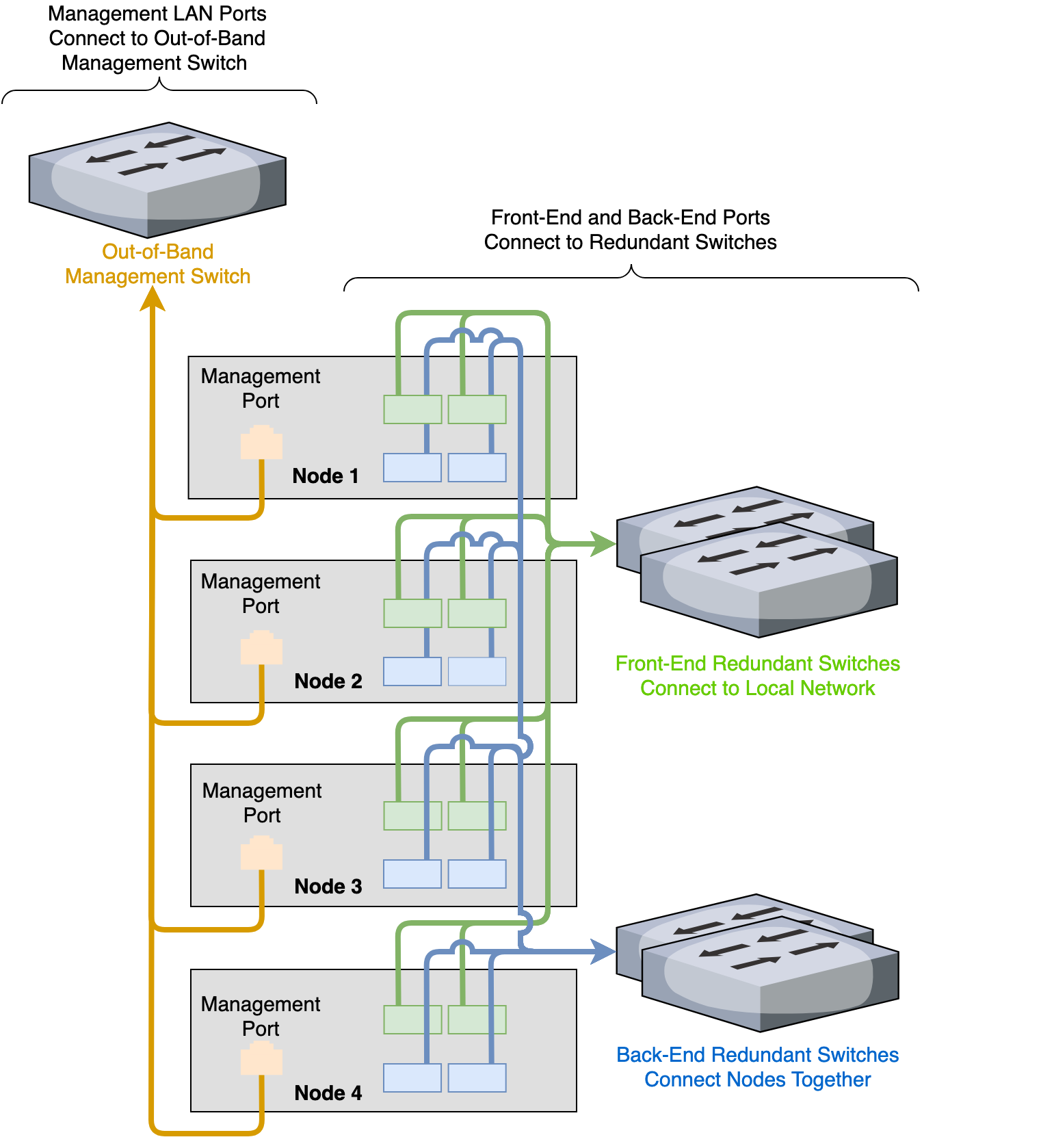
Connecting to Redundant Switches
This section explains how to connect a four-node cluster to dual switches for redundancy. We recommend this configuration. If either switch becomes inoperative, the cluster remains accessible through the remaining switch.
- Front End
- Connect the two front-end 100 Gbps ports on your nodes to separate switches.
- The uplinks to the client network must equal the bandwidth from the cluster to the switch.
- The two ports form an LACP port channel by using a multi-chassis link aggregation group.
- Back End
- Connect the two back-end 100 Gbps NIC ports on your nodes to separate switches.
- Use an appropriate inter-switch link or virtual port channel.
- MTU
- For all connection speeds, the default behavior is that of an LACP with 1,500 MTU for the front-end and 9,000 MTU for the back-end.
Connecting to a Single Switch
This section explains how to connect a four-node cluster to a single switch.
- Front End
- Each node has two front-end 100 Gbps NIC ports connected to a single switch.
- The uplinks to the client network must equal the bandwidth from the cluster to the switch.
- The two ports form an LACP port channel.
- Back End
- Each node has two back-end 100 Gbps ports connected to a single switch.
- MTU
- For all connection speeds, the default behavior is that of an LACP with 1,500 MTU for the front-end and 9,000 MTU for the back-end.
Four-Node Cluster Architecture Diagrams
The following is the recommended configuration for a four-node cluster connected to an out-of-band management switch, redundant front-end switches, and redundant back-end switches.
Important
For your node to work correctly, you must connect at least one port in the NIC.
For your node to work correctly, you must connect at least one port in the NIC.
