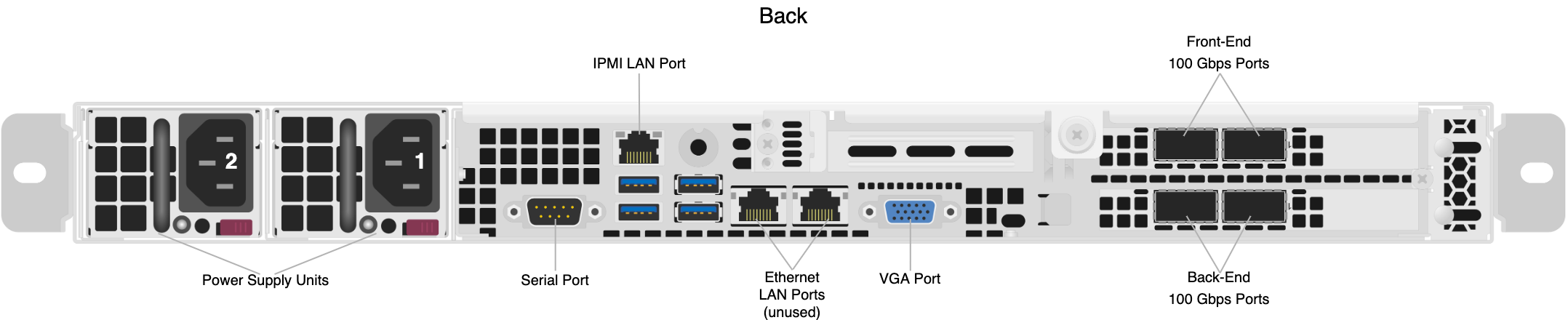
This section explains how to wire the out-of-band management (IPMI) port, 100 Gbps ports, and power on Supermicro 1114S nodes.
The Supermicro A+ WIO 1114S-WN10RT platform has reached its End of Life (EoL) on April 18, 2025. For more information about End of Platform Support (EoPS), contact Supermicro support.
This platform uses a split networking configuration in which different NICs handle back-end and front-end traffic. You can connect the front-end and back-end NICs to the same switch or to different switches.
The two rightmost Ethernet ports on the back of your node are unused.
Step 1: Connecting the Out-of-Band Management (IPMI) Port
The dedicated out-of-band management port allows functionality such as remote display, control, and power. The port uses the Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) protocol.
The IPMI port is located on the back of your node.
For more information, see Default IPMI Usernames and Passwords 🔒 on Qumulo Care.
The IPMI username and password are unrelated to your Qumulo administrative credentials.
To configure the IPMI port, you must use the IPMI Management Utility installed on the motherboard. For more information, see Supermicro BMC User Guide X12.
Step 2: Connecting the 100 Gbps Ports
After you connect the IPMI port, connect your front-end and back-end 100 Gbps ports (compatible with QSFP28 and QSFP56). There are four 100 Gbps ports on the back of your node. To maximize redundancy, split interfaces across subnets by connecting each port to a different switch.
To identify the
eth port, run the following command:for i in /sys/class/net/eth*; \
do echo $i; \
cat $i/device/uevent | \
grep -i pci_slot; \
doneStep 3: Connecting the Power
After you connect your 100 Gbps ports, connect power to the node. There are two power sockets on the back of your node. To maximize redundancy, connect each PSU to a separate power supply or power distribution unit (PDU).
